Download this post as a PDF: 42 Digital Marketing Terms for Innkeepers Cheat Sheet
One of the hardest parts about learning digital marketing for your B&B or hotel is figuring out what exactly all those strange words, phrases, and acronyms even mean. If you sometimes feel overwhelmed by the jargon or struggle to remember what each acronym stands for, you are not alone. We can’t tell you how much time we spend explaining the difference between citations and backlinks or helping customers remember terms like CTA, CPC and NAP. To help, we’ve compiled a glossary of the 42 most commonly used words & phrases all hoteliers should know.
- Alt Text/Alt Tags/Image Title Text: Descriptions of the images in your site’s HTML. Because search engines read only the alt text/alt tags and not the actual images, it is important to include them for in-line (ie - not background) images whenever possible to increase the authority of your site.
- Anchor Text: The actual text of a link to your website. It helps search engines understand the content of your site, or what the specific webpage is “about.”
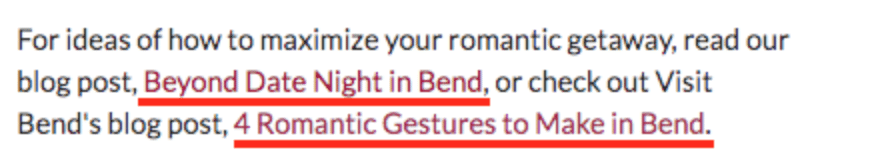
- Backlinks or Inbound Links: Any outside links to a page on your website from another website. Backlinks contribute to your website’s domain authority. See: “Why Your Website Needs Links and How to Get Them.”
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of people who visit a single page on your website and then leave within 30 seconds or without clicking onto any other pages.
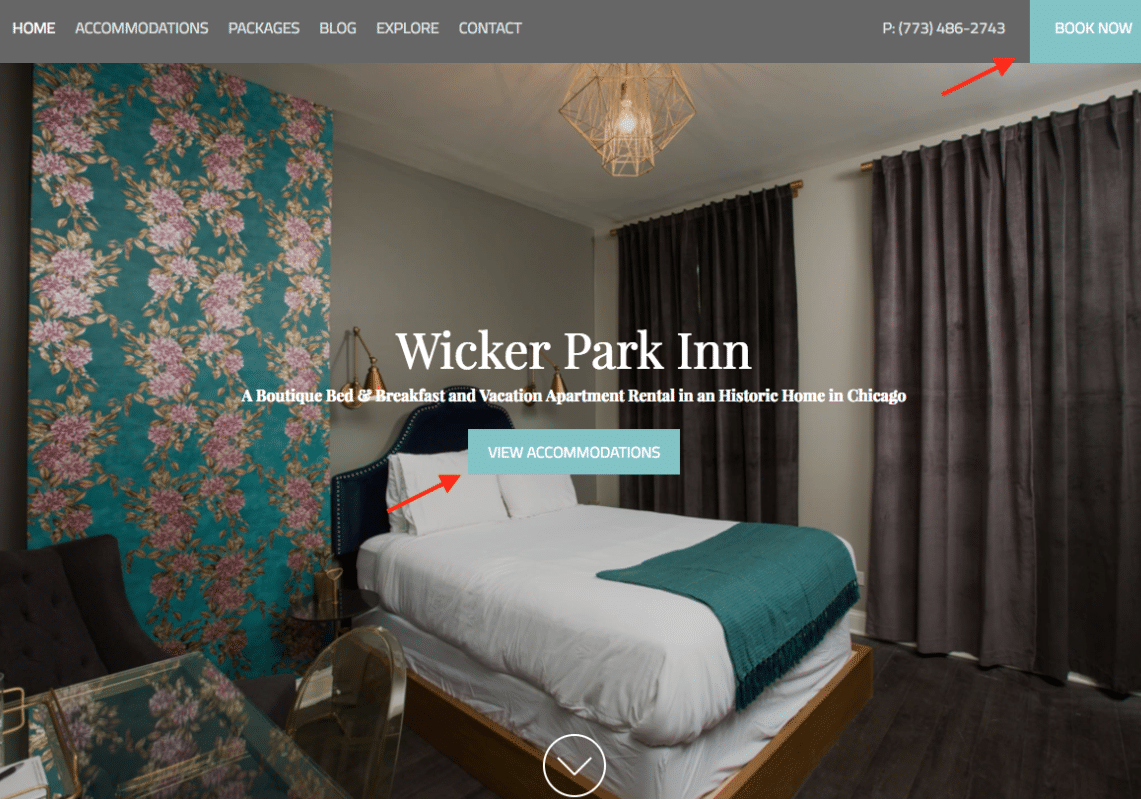
- Call to Action (CTA): Specific words or phrases on your website meant to entice visitors to make a certain action, such as a booking. Usually takes the form of a button or “call-out.”
Examples of Call to Action buttons. - Channel Manager: A software such as MyAllocator, that allows you to easily set up and coordinate rates and availability across separate channels, like TripAdvisor, Booking, and Expedia.
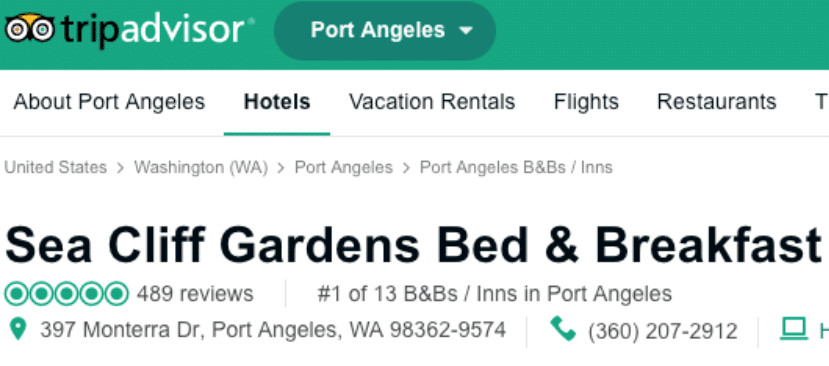
- Citations: Online references to your property’s contact information, including name, address, and phone number. Citations can improve your local search rankings even without a link to your website. An example would be a listing on TripAdvisor or BedandBreakfast.com where a link to your website doesn’t exist but your business NAP info does.
Example of a citation for Sea Cliff Gardens Bed & Breakfast on TripAdvisor including the business NAP (Name Address Phone). Note: A business listing on TripAdvisor that includes a "Hotel Website" link is still just a citation. TripAdvisor hides the actual link from Google. - Click through rate (CTR) : The percentage of your audience that advances from one part of your website to the next.
- Conversion: When a visitor to your website makes a direct booking at your property, or fulfills some other desired activity of your site.
- Conversion rate: The percentage of people who complete the desired action of a single webpage, such as making a direct booking or filling out a web form.
- Cost Per Click (CPC) : The amount of money you spent to get a digital advertisement clicked. It also refers to an advertising model where advertisers pay a publisher (aka. Google, Facebook, or a website owner) a certain amount of money each time someone clicks on their ad. (see also PPC)
- Crawled pages: The pages of your website that are found and available to search engines for indexing. Just because a page is crawled does not mean it will be indexed. (See also Indexed Pages)
- Domain: The web address of your site, also known as the URL.
- Domain Authority: A page or website’s ability to rank well in search engines based on factors like backlinks, domain age, traffic trends and history, and the amount of fresh and high-quality content your site produces.
- Google Analytics: A tool that helps you analyze the traffic to your site and better understand the type of visitors you bring to your site. Google Analytics can help you customize content based on your current audience and track the success of your latest marketing techniques.
- Headings or Headlines: The large, introductory text that describes the subject or title of a certain section of your website. Headings are divided into three sizes, from largest to smallest: H1, H2, and H3. Use subheadings to improve the readability of your web pages.
Examples of various headings and subheadings from h1 to h4 are indicated in the image above. - HTML: Short for HyperText Markup Language, a common language used to write web pages.
- Inbound Marketing: A way of drawing potential guests to your site using providing high quality content to customers at every state of their Travel Customer Journey. This includes blog posts, social media, and search engine optimization.
- Indexed Pages: The pages on your website that are actually stored by search engines to be used in search results (a page can be ‘crawled’ but not ‘indexed). (See also Crawled Pages)
- Internal Links: Links that allow visitors to easily navigate from one page to the next within your own site, such as from the Homepage to the Rooms page. Internal links may or may not use “anchor text.”
- Keywords: The topics or ideas that best define what your website is about. These are the terms that people enter into search engines to arrive at your site.
- Link Building: The process of collecting links from outside websites that take visitors back to your own site. High-quality links matter more than high quantity of links. Examples of inbound links might be a link from your association or chamber of commerce website. See: “Why Your Website Needs Links and How to Get Them.”
- Local Listing: The websites and online directories that contain your hotel name, address, and phone number. Local listings can be found on sites like Google My Business, Yelp, and Internet Yellow Pages and data aggregators like Acxiom. The more places you are listed, the better your visibility to travel customers and the more search engines trust the accuracy of your data. Make sure this data is the same across all profiles.
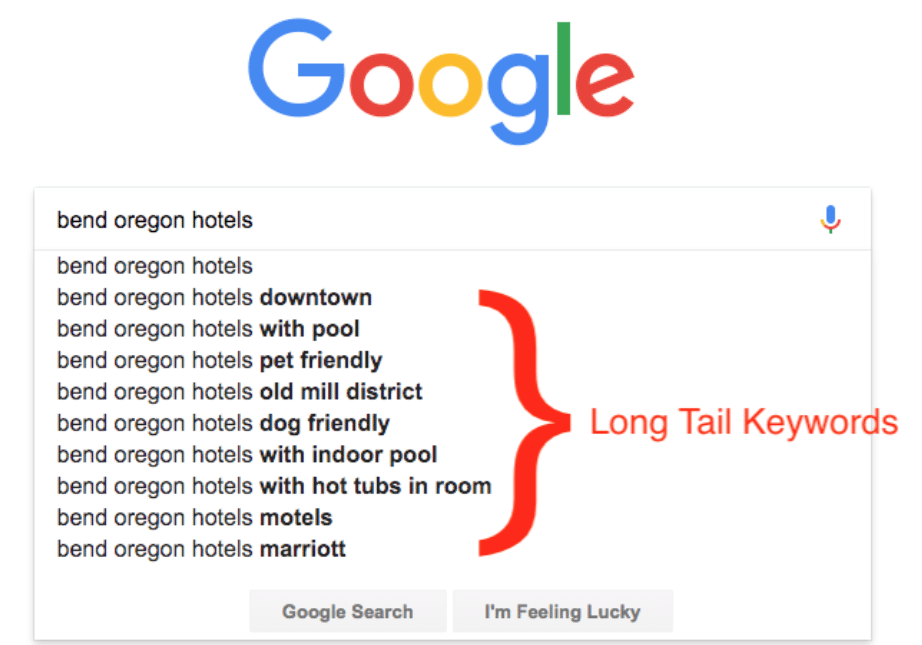
- Long Tail Keywords: A three or four-word or longer search phrase meant to target a specific topic, demographic or interest. They are generally less common and competitive than shorter keywords but can help you attract a certain desired audience.
Examples of Long Tail Keywords for "bend oregon hotels" shown above. - Meta Descriptions: A short & informative description (about 150-160 words) of the webpage’s content. It is displayed below the page title on the Search Engine Results Page. Though meta descriptions aren’t used in search engine ranking algorithms, they are still a critical factor in encouraging users to click on to your site. If you can, always include a Call to Action (such as Book direct now!) in your meta description.
- NAP: Your business Name, Address, and Phone Number. NAP in your citations and local search listings is used by search engines to help with rankings. Ensure that your NAP is consistent across all sites and directories to make it easier for search engines to rank your business well.
- On-Page SEO: The practice of optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and bring more traffic to your site. Important factors of on-page SEO include quality content, site structure, keyword use & placement, meta descriptions, meta keywords, and internal links.
- Off-Page SEO: Any activity done outside of your website that works to improve your rankings and domain authority. Building your off-page SEO is pretty much like building your online reputation. Consider things like backlinks, citations, local business listings, and press releases.
- Online Travel Agency (OTA): Directory-style websites where visitors can book a stay at your property without visiting your website. OTA’s charge you a commission fee for every booking made through your site. Popular OTAs include Expedia, Booking.com, TripAdvisor, Agoda, and Trip.com.
- Page Speed: The time it takes to fully display everything on a certain webpage, also known as “page load time.”
- Pay Per Click (PPC): The amount of money you spent to get a digital advertisement clicked. It also refers to an advertising model where advertisers pay a publisher (aka. Google, Facebook, or a website owner) a certain amount of money each time someone clicks on their ad. (see also CPC)
- Property Management System (PMS): A software application that coordinates and manages operational functions such as bookings, sales, financial reporting, etc.
- Return on Ad Spending (ROAS): A marketing metric used to measure the efficiency of your marketing campaign.
- Return on Investment (ROI): A way of measuring how efficient and profitable an online advertisement is relative to its cost. Use this formula: Gain from investment-Cost of investment/Cost of investment.
- Search Engine Marketing (SEM): Sometimes used to refer to the practice of managing search engine advertising (Google AdWords), but is also used to refer to the entire practice of marketing your website in search engines, including both paid and organic placements.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): The process of increasing the quality and quantity of traffic to your website by ensuring that it ranks highly on search engines. SEO requires execution across several aspects of your website and online presence.
Remember, search engine optimization is about more than just keywords. - Search Engine Results Page (SERP): The page displayed by a search engine after you type in your query. The SERP includes organic search results, paid results, and advertisements.
- Sitemaps: Index documents that list the pages on your website accessible to crawlers or users. They demonstrate the organization, navigation, and labeling system of your site.
- Title Tags: The title of a page of your website. These are the words that appear in search engine results and at the top of a user’s web browser when they are on a certain page. Both search engines and internet users look at title tags to see what your page is about.
- URL: Your web address, ie. www.myhotel.com
- User Experience (UX): An evaluation of how positive or negative a visitor’s experience of your website was. Consider things like website design, page speed, clarity and quality of content, mobile friendliness, and so on.
- Year Over Year (YOY): A way of measuring performance annually. Especially helpful in a seasonal business (like hospitality) to determine growth where month-to-month statistics don’t properly tell the story.
We hope this glossary has helped you to better understand all the need-to-know online marketing terminology. Download our PDF to have on hand for reference whenever you need a quick reminder.